- by x32x01 ||
When data travels over the internet, it typically uses one of two main protocols: UDP (User Datagram Protocol) or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). Both handle how information moves from your computer to servers and back, but they work very differently. Knowing the difference is essential for developers, network engineers, and anyone interested in cybersecurity or network optimization. 
What is UDP?
UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol. It’s designed for speed and simplicity.
This simple example sends a UDP message to a server. Notice there’s no handshake - data is just sent.
What is TCP?
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol. Unlike UDP, TCP is reliable and connection-oriented.
Notice here we establish a connection first, which guarantees the message is delivered reliably.
UDP vs TCP: Key Differences
In simple words:
Why It Matters for Developers & Security Professionals
Understanding UDP and TCP helps in:
Advanced Tips: When to Prefer UDP Over TCP and Vice Versa
Example: Streaming vs File Download Scenario
Security Considerations
Summary: Make the Right Choice
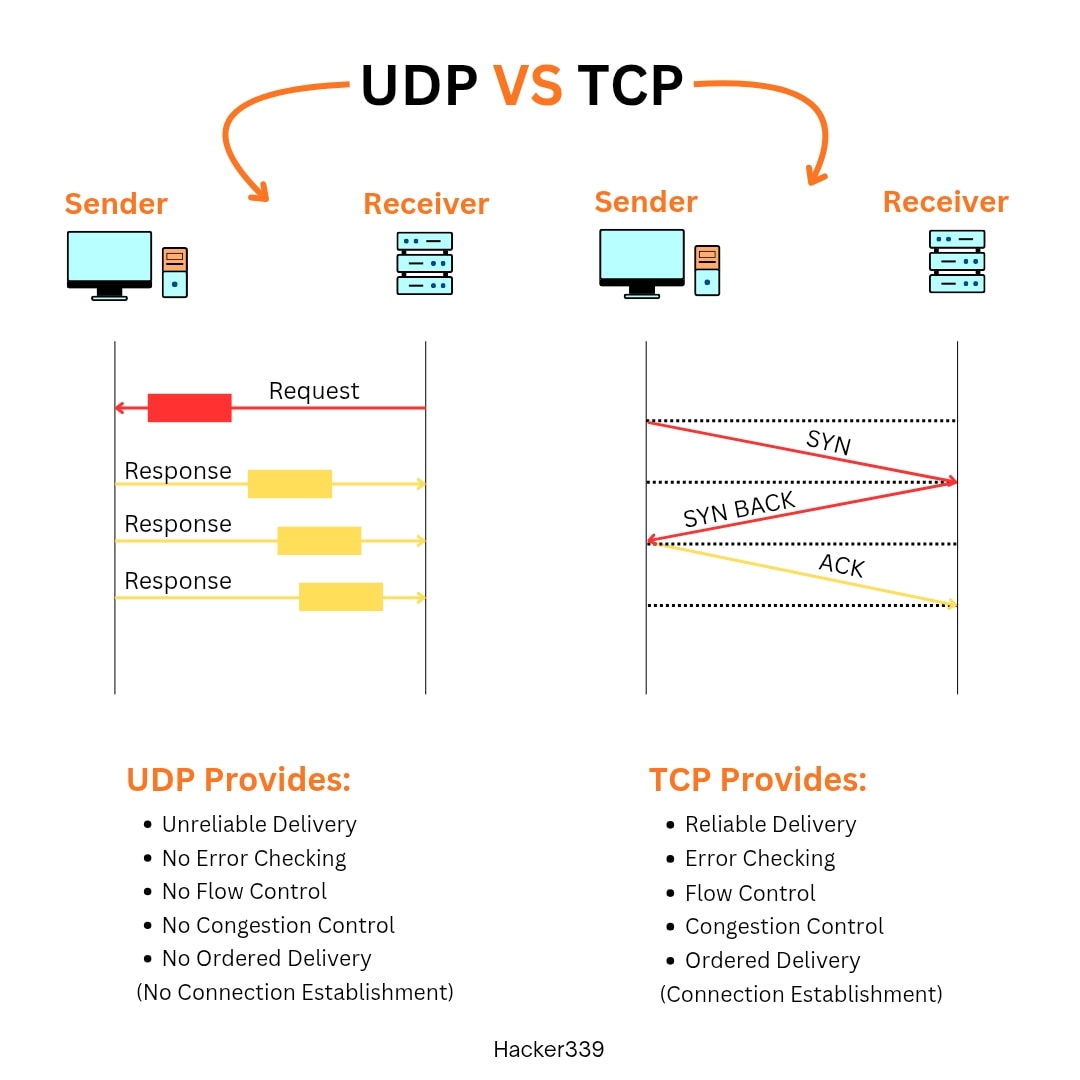
What is UDP? 
UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol. It’s designed for speed and simplicity.Key Features of UDP:
- No connection required
 - data is sent without establishing a session.
- data is sent without establishing a session. - Very fast
 - great for real-time applications.
- great for real-time applications. - No error checking
 - packets may be lost, and you won’t always know.
- packets may be lost, and you won’t always know. - No flow or congestion control
 - the sender can overwhelm the network if not careful.
- the sender can overwhelm the network if not careful. - No ordered delivery
 - packets may arrive out of sequence.
- packets may arrive out of sequence.
When to Use UDP:
UDP is perfect for applications where speed is more important than reliability:- Live streaming
 - video and audio need low latency.
- video and audio need low latency. - Online gaming
 - missing a few packets won’t ruin the game.
- missing a few packets won’t ruin the game. - Video calls & VoIP
 - real-time communication tolerates minor losses.
- real-time communication tolerates minor losses.
Example: Sending a UDP Packet in Python
Python:
import socket
udp_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
server_address = ('127.0.0.1', 12345)
message = b"Hello UDP!"
udp_socket.sendto(message, server_address)
udp_socket.close()What is TCP? 
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol. Unlike UDP, TCP is reliable and connection-oriented.Key Features of TCP:
- Connection establishment
 - uses SYN and ACK handshake to start communication.
- uses SYN and ACK handshake to start communication. - Reliable & ordered delivery
 - ensures all data arrives in the correct sequence.
- ensures all data arrives in the correct sequence. - Error checking
 - corrupted packets are detected and retransmitted.
- corrupted packets are detected and retransmitted. - Flow and congestion control
 - prevents network overload and slows down if necessary.
- prevents network overload and slows down if necessary.
When to Use TCP:
TCP is best for applications where data integrity matters more than speed:- Web browsing
 - ensures pages load correctly.
- ensures pages load correctly. - Emails
 - messages must arrive complete.
- messages must arrive complete. - File downloads/uploads
 - no missing or corrupted parts allowed.
- no missing or corrupted parts allowed.
Example: Sending a TCP Packet in Python
Python:
import socket
tcp_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
tcp_socket.connect(('127.0.0.1', 12345))
tcp_socket.send(b"Hello TCP!")
tcp_socket.close()UDP vs TCP: Key Differences 
| Feature | UDP | TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | None | Required (SYN, ACK) |
| Speed | Very fast | Slower |
| Reliability | Low | High |
| Error Checking | No | Yes |
| Packet Order | Not guaranteed | Guaranteed |
| Flow Control | No | Yes |
| Best for | Streaming, Gaming, Video Calls | Web, Email, Files |
In simple words:
- UDP = Fast but risky


- TCP = Slower but safe


Why It Matters for Developers & Security Professionals 
Understanding UDP and TCP helps in:- Optimizing applications - choose the right protocol for your use case.
- Troubleshooting networks - recognize why some packets are lost or delayed.
- Improving security - certain attacks exploit TCP’s handshake (SYN floods) or UDP’s lack of connection (UDP floods).
- Performance tuning - adjust flow control and packet size for better efficiency.
Advanced Tips: When to Prefer UDP Over TCP and Vice Versa 

Choose UDP if:
- You need low latency and can tolerate occasional data loss.
- Real-time performance is critical (streaming, online gaming).
- The application implements its own error correction.
Choose TCP if:
- Data integrity is critical (financial transactions, emails).
- You cannot tolerate lost packets or out-of-order delivery.
- You want built-in flow and congestion control.
Example: Streaming vs File Download Scenario 

- Streaming a movie: UDP allows continuous playback even if some packets drop. Missing frames are negligible compared to buffering delay.
- Downloading a software update: TCP ensures all data is received correctly. A single missing packet could corrupt the installation.
Security Considerations 
- UDP vulnerabilities: No handshake means it’s easier to spoof addresses, making DDoS amplification attacks possible.
- TCP vulnerabilities: Handshake can be exploited with SYN flood attacks, requiring mitigation via firewalls or rate-limiting.
- Firewalls & monitoring: Often treat UDP and TCP traffic differently. Network admins should be aware when opening ports.
Summary: Make the Right Choice 
- UDP = Speed over reliability. Great for real-time apps where latency matters.
- TCP = Reliability over speed. Perfect for transactions, emails, and file transfers.
- Understanding the trade-offs ensures better application performance, network stability, and security.
Last edited: